Live Reloading and Lazy Loading Micro-Frontends using Ara Framework
Demo code here.
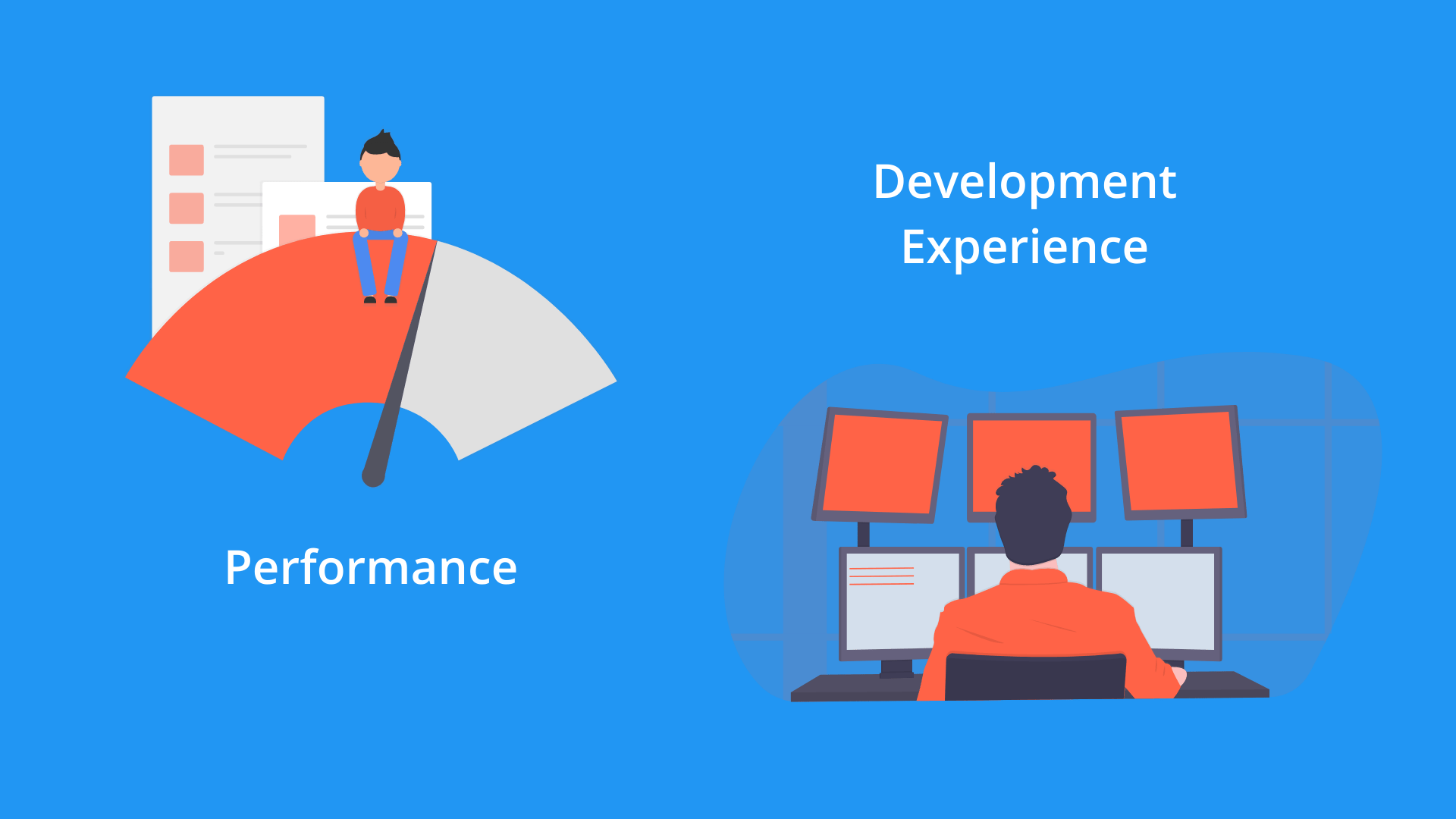
Micro-frontends solve some organizational and technical problems, nevertheless, they could cause other ones. As software architects we need to take decisions to solve the most critical problems and figure out how to mitigate the new ones caused by the chosen solution.
True success requires sacrifice — Rick Riordan
In this article, we'll learn how to mitigate some of them.
Network Overload (Performance issues)
Micro-frontends can deliver its JavaScript bundle independently. However, the host application needs to download a file for each Micro-Frontend it consumes. In the worst scenario, it could need to download a bunch of files affecting the performance for its initial load.
Refresh Host Page (Developer experience issues)
Another issue comes during the development cycle. For a Monolith Frontend application is easy to refresh the page any time the code changes using a live reload tool. However, for Micro-frontends this task becomes more difficult because the host application only consume the JavaScript bundle for each Micro-Frontend and their underlying code is outside its boundaries.
Webpack Nova Consumer
We created webpack-nova-consumer to tackle the problems mentioned above. This plugin supports live reloading across Micro-Frontends(Novas) and lazy loading for the JavaScript bundles in production mode.
We'll see it in action later through this article.
Set Up Host Application (Nuxt SPA)
First, create a Nuxt application in spa mode:
Note: Choose Single Page App for the Choose rendering mode option.
create-nuxt-app nuxt-spa
Inside the folder nuxt-spa, run the nuxt application in http://localhost:3000:
yarn dev
Browser:

After running the application we'll see a page rendering the example page for nuxt.
Set Up Micro-frontend (Foo Nova)
Create a new Nova using the CLI:
Note: Type n when the Do you want to include Server-Side Rendering (SSR) option appears to include only the client-side entry point.
ara new:nova -t vue foo-nova
For production, we need to build the client-side entry point and deploy it in a storage service such as Amazon S3 and distribute it through a CDN. However, for development, we'll serve it using webpack-dev-server.
Serve the JavaScript bundle in http://localhost:8080/client.js
yarn dev
Notice, the foo-nova/src/components folder contains a component named Example that is used in the entry point foo-nova/src/index.js file. We'll render it in the nuxt application next.
Implement Micro-frontend (Foo Nova) in Nuxt
First, we need to install the Nova Bridge for Vue.js. This package provides a component to include Nova views inside Vue.js based applications.
yarn add nova-vue-bridge
Update the file pages/index.vue with the following code:
<template>
<div class="container">
<logo />
<nova name="Example" :data="{ title: 'Ara Framework' }"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Nova from 'nova-vue-bridge'
import Logo from '~/components/Logo.vue'
export default {
components: {
Logo,
Nova
}
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
margin: 0 auto;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
Run the nuxt application again:
yarn dev
Browser:

After running the application the page shows only the Nuxt logo because we're not loading the JavaScript bundle for the Foo Nova yet. However, if we inspect the HTML elements in the browser we can notice the Nova Bridge renderers the placeholder where the Micro-frontend (Nova) view will be mounted.
<div data-hypernova-key="Example" data-hypernova-id="8f07d513-0c84-4b16-8058-08cf2a014d0d"></div>
<script type="application/json" data-hypernova-key="Example" data-hypernova-id="8f07d513-0c84-4b16-8058-08cf2a014d0d"></script>
Load JavaScript bundle using Webpack Nova Consumer
Install webpack-nova-consumer in nuxt application.
yarn add --dev @ara/webpack-nova-consumer
After installing the package, import the NovaConsumer plugin and add it inside the extend section in the nuxt.config.js file.
nuxt.config.js
import NovaConsumerPlugin from '@ara/webpack-nova-consumer'
export default {
...
build: {
/*
** You can extend webpack config here
*/
extend (config, ctx) {
config.plugins.push(new NovaConsumerPlugin({
novas: [
{
entry: 'http://localhost:8080/client.js',
views: [
'Example'
]
}
]
}))
}
}
}
The NovaConsumerPlugin receives an object with the information of the Micro-frontends (Novas) it's consuming:
entry: JavaScript bundle that contains the entry point for the Micro-frontend.views: List of view names that the Micro-frontend supports.
Browser:

After running the nuxt application again we'll see the Micro-Frontend rendered.
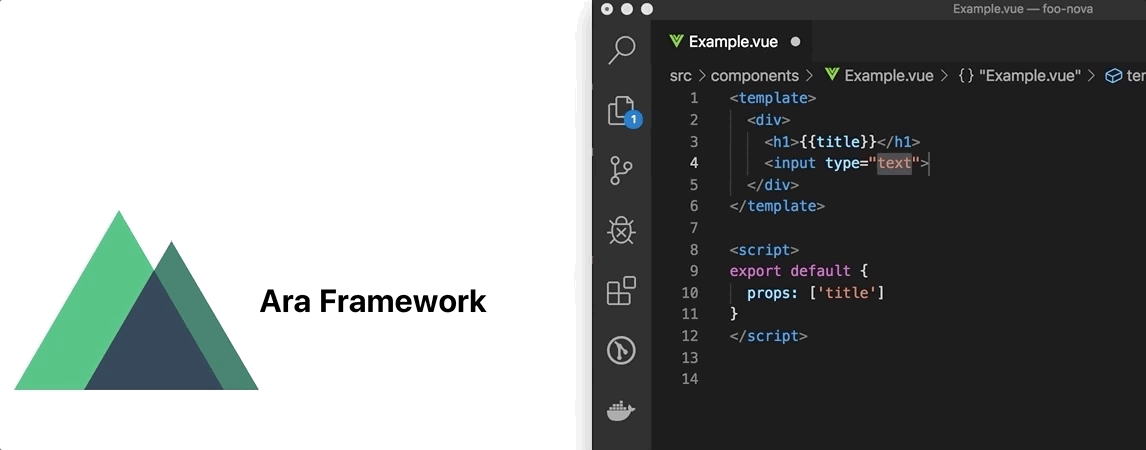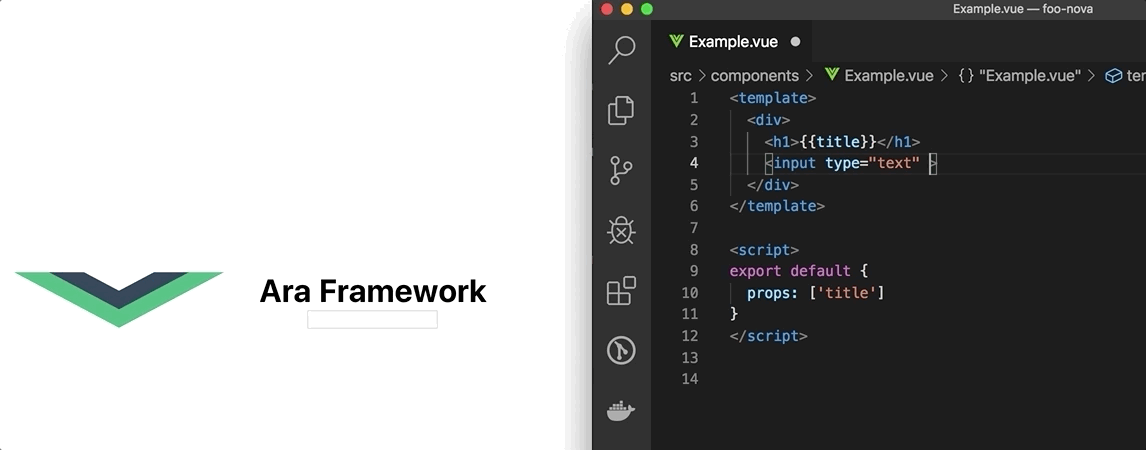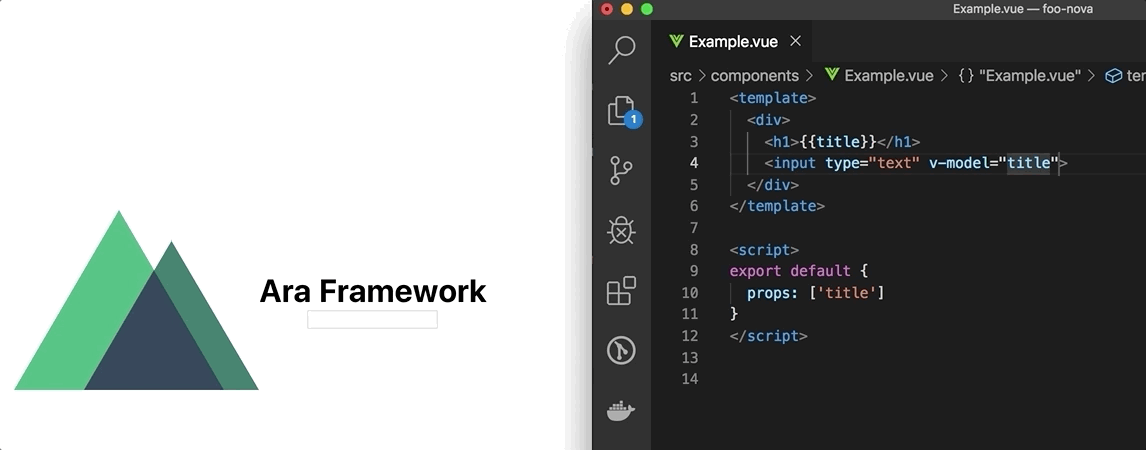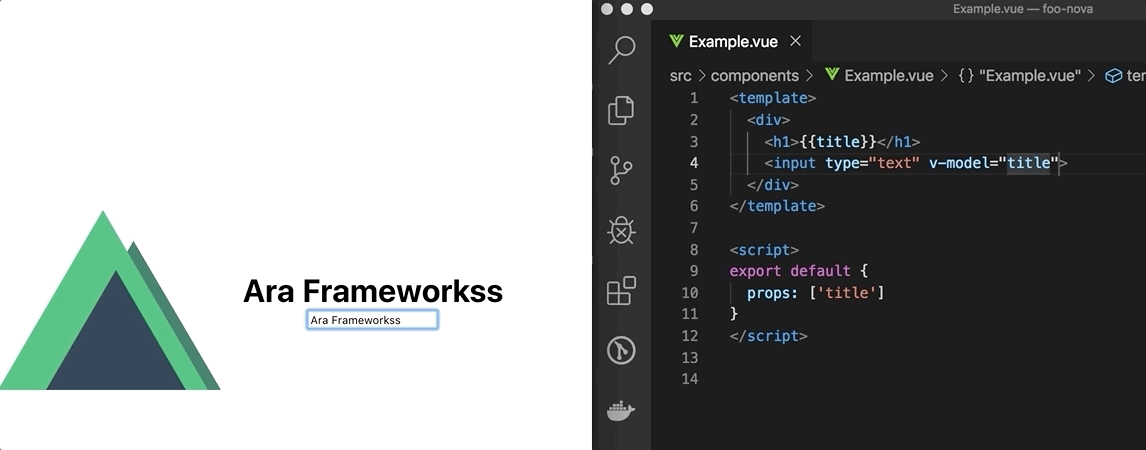
Live Reloading
Now, we can update the Example.vue component in the foo-bar/components folder and the host application (nuxt) will reaload the page showing the latest changes.
Update Example.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="title">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['title']
}
</script>
Live Reloading in action:
Set Up Micro-frontend (Bar Nova)
In order to test our nuxt application using more than one Micro-frontend we'll create a new one named bar-nova.
Create a new nova following the same steps mentioned before.
ara new:nova -t vue bar-nova
Change the view name from Example to Bar in src/index.js:
import { load, Vue, mountComponent, loadById } from 'hypernova-vue'
import Example from './components/Example.vue'
const render = (name, { node, data }) => {
if (name === 'Bar') {
return mountComponent(Vue.extend(Example), node, data)
}
}
document.addEventListener('NovaMount', ({ detail }) => {
const { name, id } = detail
const payload = loadById(name, id)
if (payload) {
render(name, payload)
}
})
load('Bar').forEach(render.bind(null, 'Bar'))
Serve the JavaScript bundle in http://localhost:8081/client.js
yarn dev
Implement Micro-frontend (Bar Nova) in Nuxt
We need to create a new page named bar where we'll implement the Bar view. we'll also add a link in the main page to navigate to the bar page.
Create a new page pages/bar.vue:
bar.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div>
<logo />
<nova name="Bar" :data="{ title: 'Bar Page' }"/>
</div>
<div>
<nuxt-link to="/">Main Page</nuxt-link>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Nova from 'nova-vue-bridge'
import Logo from '~/components/Logo.vue'
export default {
components: {
Logo,
Nova
}
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
margin: 0 auto;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
Add a link to the bar page in the pages/index.vue file:
index.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div>
<logo />
<nova name="Example" :data="{ title: 'Ara Framework' }"/>
</div>
<div>
<nuxt-link to="/bar">Bar Page</nuxt-link>
</div>
</div>
</template>
Add new entry point in the nuxt.config.js file:
import NovaConsumerPlugin from '@ara/webpack-nova-consumer'
export default {
...
build: {
/*
** You can extend webpack config here
*/
extend (config, ctx) {
config.plugins.push(new NovaConsumerPlugin({
novas: [
{
entry: 'http://localhost:8080/client.js',
views: [
'Example'
]
},
{
entry: 'http://localhost:8081/client.js',
views: [
'Bar'
]
}
]
}))
}
}
}
Browser:

After running the nuxt application again we'll see the views are rendered navigating from one page to other. We'll test the lazy loading feature next.
Lazy Loading
Lazy loading is enabled automatically using webpack in production mode. The plugin adds a nova-lazy-load script in the built app. Behind scenes, this script listens to the NovaMount event emitted by Nova Bridge in order to load the JavaScript bundle that mounts the requested view.
Build nuxt application:
yarn build
Install http-server to serve the static files:
npm i -g http-server
Go to the dist folder and serve the static files in http://127.0.0.1:3000:
http-server . -p 3000
Browser:

Notice, the JavaScript bundle for the Bar Micro-frontend is loaded only when the user navigates to the bar page. In general, the Nova bundles are only loaded when one of their views is placed on the page.
